
Hydroacoustic technology
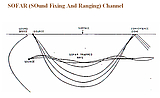
SOFAR (SOund Fixing And Ranging) Channel.
The term hydroacoustics describes the study of sound waves in the water and its applications. Hydroacoustic monitoring involves recording signals that show changes in water pressure generated by sound waves in the water.
Sound propagates very efficiently through water so that it can be heard and detected at great distances. There is one layer in the water where sound travel is slower but particularly efficient. This layer is the Sound Fixing and Ranging Channel, SOFAR, which is typically at a depth of about 1000 m. Hydroacoustic monitoring makes use of the unique phenomenon of sound waves being trapped in that layer.
Hydroacoustic technology first evolved at the beginning of the 20th century with the aim of increasing safety of sea travel. Sound waves were emitted and their reflections measured off objects such as icebergs and shoals in the water. Called sonar (sound navigation and ranging), this technology was soon used for submarine navigation and detection.

USS Greeneville, US Navy submarine.
Apart from military application, this technology is of great use in a range of civil and scientific fields. Hydroacoustic technology helps in the research of whale populations and their migration patterns, in climate change studies and intsunami warning systems. The technology also continues to be used where it first started, namely in increasing shipping safety.
我想说两句