
How is sound used to study undersea earthquakes an
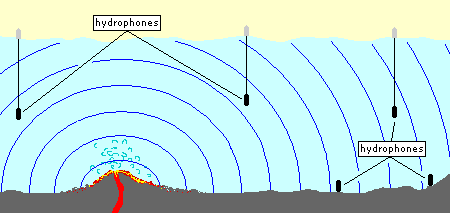
Undersea earthquakes and volcanic eruptions (seismic events) make low frequency sounds. The sounds they make can be heard far away from the seismic event location. In the Pacific Ocean, sounds from a volcanic eruption have been heard thousands of miles away. Hydrophones located around the Pacific Ocean monitor the ocean for sounds of seismic events. The sounds made by a seismic event are also used to accurately locate the event. Very small eruptions can be monitored and located with sound. These small eruptions far from land can be difficult to monitor and locate with seismometers on land.
Earthquakes not associated with volcanic eruptions make different sounds than volcanic eruptions. Using the sounds made by the seismic event, scientists can tell if the event is an earthquake or a volcanic eruption.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) VENTS Program uses the Navy's Sound Surveillance System (SOSUS) and additional hydrophones to monitor the North Pacific Ocean and the North Atlantic Ocean for seismic events.
我想说两句